All You Need to Know About Carbon Fiber for 3D Printing
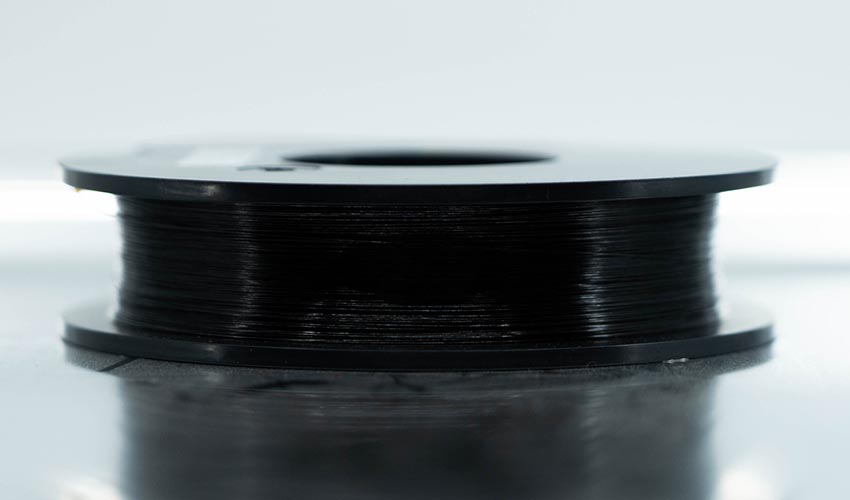

The advent of 3D printing has brought about a transformative revolution in the fields of design and manufacturing. And now, with the emergence of 3D printed carbon fiber composites, a whole new realm of possibilities is unfolding. Carbon fiber, which was originally introduced by Joseph Swan in 1860, is composed of a long chain of interconnected carbon atoms. Typically, this chain has a diameter ranging from 5 to 10 micrometers, with its length varying depending on its intended use. In this comprehensive guide, you will discover valuable insights on the contemporary utilization of carbon fiber, including its applications, the manufacturers offering this material, and the reasons behind its widespread adoption.
Carbon Fiber Properties
As we are aware, carbon fibers are seldom used in isolation. Typically, they are combined with other materials to create composites, specifically referred to as carbon fiber-reinforced materials in this instance. These composites consist of a matrix material, typically a polymer, to which carbon fibers are added, although non-polymeric materials like ceramics can also be utilized. The primary advantage lies in manufacturing stronger yet lighter components with heightened rigidity. The mechanical properties of 3D printed carbon fiber composites surpass those of nearly all other 3D printed plastics in terms of toughness and temperature resistance.
Filaments incorporate short carbon fibers, consisting of segments less than a millimeter in length, that are blended with a thermoplastic known as the base material. Various popular filaments are available with carbon fiber fillers, including PLA, PETG, nylon, ABS, and polycarbonate. These fibers possess exceptional strength, thereby enhancing the filament’s strength and stiffness while reducing overall weight.
Over time, carbon fiber has gained significant popularity in diverse industries due to its exceptional properties such as high stiffness, tensile strength, low weight, chemical resistance, capacity to withstand high temperatures, and low thermal expansion. Notably, pure carbon fiber is five times stronger and twice as stiff as steel, despite being lighter. These characteristics render carbon fibers suitable for applications that rely on material properties to optimize performance, particularly in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, military, and civil engineering, among others.
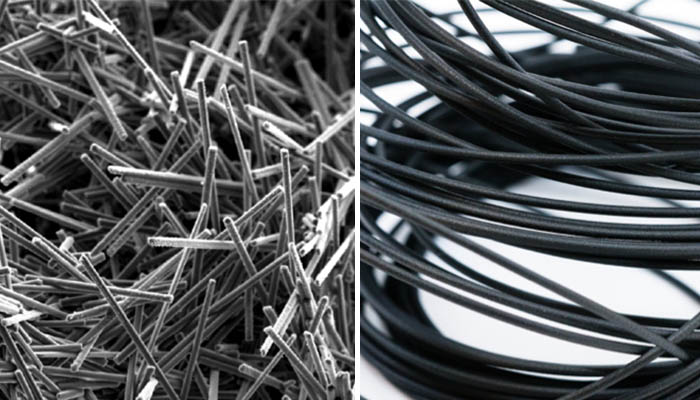

Carbon fiber segments are incorporated into the filament for reinforcement | Credits: Markforged
Carbon Fiber 3D Printing
The requirements for 3D printing carbon fiber filaments should align with those of the base material they are combined with. The key distinction is that the fibers can cause nozzle blockages in the 3D printer, prompting experts to recommend using a hardened steel nozzle. Additionally, when the fiber content surpasses a certain threshold, the surface finish of the 3D printed object may be compromised.
In the realm of 3D printing, carbon fiber can be utilized in two primary ways: through carbon fiber reinforced filaments or continuous carbon fiber reinforcement. Carbon fiber filament, which has been reinforced, offers greater strength compared to unreinforced filament. However, for even stronger parts, an alternative technique called continuous carbon fiber reinforcement can be employed. This method involves the use of two nozzles: one extrudes the filament, and the other extrudes the carbon fiber. Since the continuous carbon fiber is not cut into smaller segments, it retains a higher level of strength. Remarkably, continuous carbon fiber 3D printing is robust enough to substitute aluminum, while weighing only half as much. 3D printer manufacturers claim that it can even replace metal 3D printing in certain applications due to its cost-effectiveness. Lastly, strategically placing carbon fiber according to additive manufacturing design techniques allows for further enhancement of part strength while reducing material consumption.
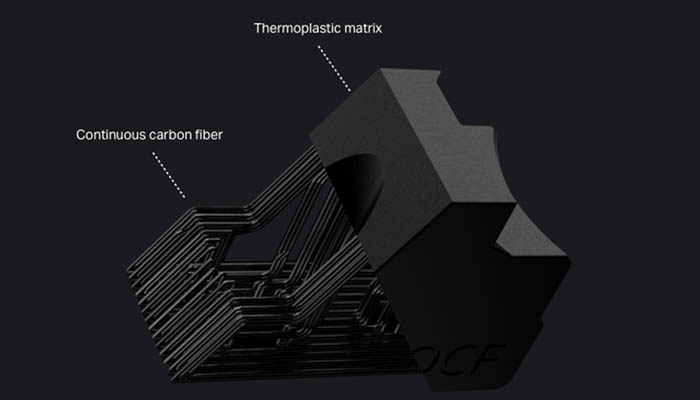
This part shows how continuous fiber 3D printing can add strength to a plastic part | Credits: Markforged
Applications
Traditionally, carbon fiber composites have been used for structural design, where added weight translates to higher life-cycle costs or unsatisfactory performance. Carbon fiber composites can be used to create many products, such as bicycle frames, aircraft wings, propellers, automotive components, and more. As you can imagine, given the numerous benefits of carbon fiber, it is no longer solely traditional manufacturing systems that utilize it. In recent years, an increasing number of 3D printing companies have been offering carbon fiber reinforced materials or technologies. They have developed the capability to work with this composite, enabling high-performance applications as they are able to withstand high temperatures and rapidly create customized shapes efficiently. Moreover, they bypass machining or molding processes, simplifying the production of custom parts, spare parts, and functional prototypes.
In their report “3D Printing Composites 2020-2030,” IDTechEx reveals that the global 3D printing composites market will reach a value of $1.7 billion by 2030. This figure includes other composites such as materials reinforced with fiberglass or plastics. However, the trend clearly shows that the additive manufacturing industry is increasingly utilizing all types of composites, including carbon, in their production activities.
In conclusion, 3D printed carbon fiber parts are highly versatile for a wide range of applications. They are tough, lightweight, and can withstand impacts, heat, and chemicals. For instance, 3D printed parts made of plastic and carbon fiber composites can endure the heat generated by automobile and aircraft engines. They can also replace machined aluminum parts and manufacturing fixtures.
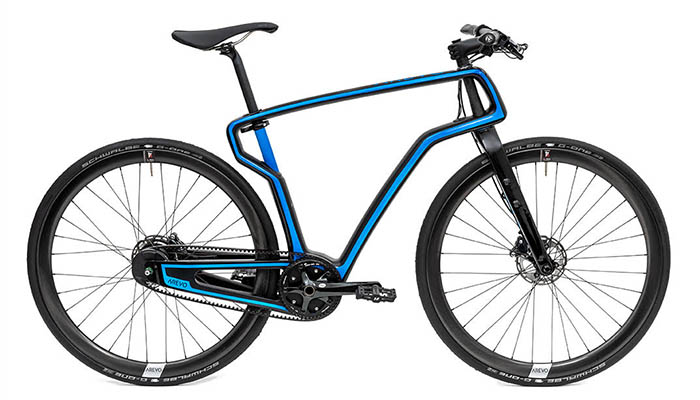

The body of this bicycle frame is made of carbon fiber | Credits: Arevo
Manufacturers and Price
Several players in the market offer technologies that enable continuous printing of this material. Markforged markets it as “Continuous Filament Fabrication” (CFF), while Anisoprint refers to it as “Composite Fiber Coextrusion” (CFC). More recently, Desktop Metal has also entered the race with their new system called Fiber, which utilizes automated microfiber placement (μAFP). Additionally, 9TLabs has developed an additional system for conventional 3D printers, which they call Additive Fusion Technology (AFT).
Certain companies have developed carbon fiber filaments specifically for technical applications. These filaments utilize high-performance polymers such as PEEK or PEKK as their base materials. As a result, they offer not only benefits like durability and strong mechanical and chemical performance but also an improved strength-to-weight ratio. Printing parameters need to be adjusted accordingly, as these polymers require extruders capable of reaching temperatures around 400°C, along with systems equipped with heated chambers and build plates. Some of the manufacturers of carbon filaments include Roboze, 3DXTech, ColorFabb, Markforged, Kimya, Intamsys, Zortrax, and more.
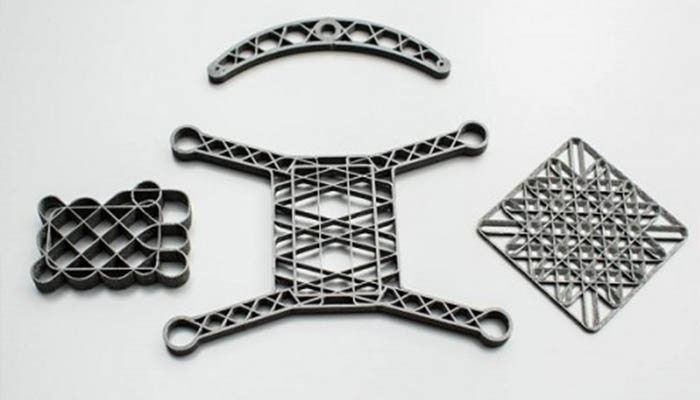

Using design techniques, it is possible to reinforce a part | Credits: Anisoprint
Stepping away from the more familiar extrusion process, one intriguing technology is AREVO’s patented approach based on Direct Energy Deposition technology. This method involves using a laser to simultaneously heat the filament and carbon fiber while a roller compresses the two together. Impossible Objects and EnvisionTEC have also incorporated systems for continuous fiber 3D printing into their lineup of machines, although their technology differs somewhat. They employ a lamination process, weaving sheets of fiber into the print. Lastly, Continuous Composites utilizes a hybrid technology where the fiber yarn is saturated with resin and then cured with UV light, similar to stereolithography 3D printing.
What do you think of carbon fiber? Would you start a project to bring back coral restoration in your area? Let us know in a comment below or on our Linkedin, Facebook, and Twitter pages! Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter here, the latest 3D printing news straight to your inbox! You can also find all our videos on our YouTube channel.








What 3D printer company provide motor bike carbon fiber chassis print?
can you suggest some printers which are capable of printing carbon fiber effectively. as i need it for drones
I am developing one. please inform me of a few requirements you have so that I can keep those in mind when designing