All You Need to Know About TPU for 3D Printing
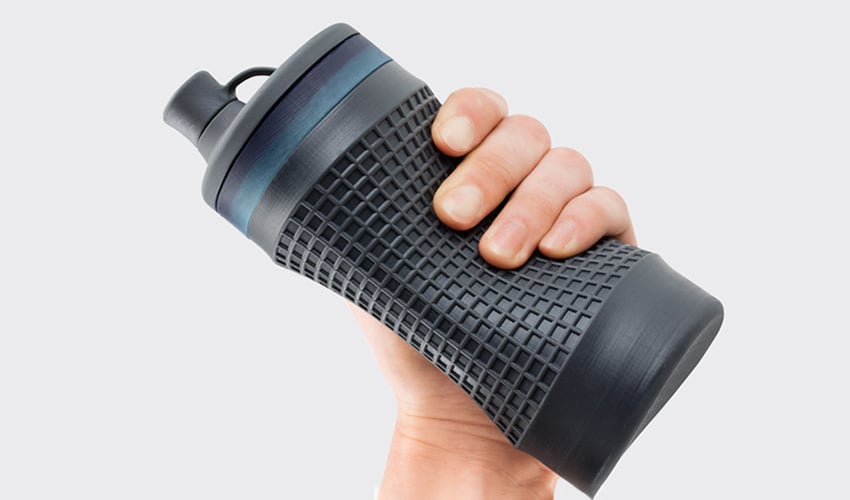

Thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) is an elastomer (synthetic plastic) that is characterized by its high flexibility and resistance during further processing and combines the properties of thermoplastics and elastomers. It can withstand much higher compressive and tensile forces than other common materials such as PLA and ABS. The reason for the variation in its softness and hardness is due to its chemical composition: Depending on the proportion of hard and soft segments, the hardness and flexibility of the material also changes. A lower filling quantity can also result in a more flexible 3D-printed part. This affects the transparency of the final parts, the softness to the touch or the adhesion of the parts. TPU is a very versatile polymer that imparts a very multi-layered set of properties to parts. TPU also offers greater resistance to all greases and oils. But what to consider when using TPU?
Production and Characteristics
Although we usually talk about TPU filaments, we can also find them in powder or resin form. In terms of the properties of these polymers, they have many benefits, including their high impact-, wear-, abrasion- and cut-resistance. They also have a relatively high layer cohesion, which results in excellent mechanical homogeneity of the manufactured parts and makes them isotropic.

Due to its flexibility, TPU is often used for the production of cell phone cases
However, there are certain limitations to this type of material that must be considered. TPU does not adapt well to hot environments. This factor is noticeable because they cannot withstand high temperatures despite their large working range. In addition, print settings should vary depending on the technology and 3D machine used. Compared to TPE, another flexible filament, TPU is easier to print and retains its elastic properties better at lower temperatures. TPU material offers better resistance to abrasion, oil and grease. Unlike stiffer thermoplastics, TPU filament has properties such as flexibility and conformability and has no problems with deformation and delamination during the 3D printing process.
3D Printing with TPU Filaments
When printing parts with TPU using an FDM printer, we recommend applying a thin layer of adhesive to the print bed, which helps the material to stick. Also, the extrusion nozzle should reach a temperature between 210 °C and 235 °C to properly melt the filament (although this depends on the manufacturer). However, these are only general tips. The success of printing with TPU depends on the configuration of each 3D printer and proper calibration. Therefore, it is recommended to perform small tests with this material before starting more complex prints. It is important to note that the extrusion system must be able to process flexible and compressible materials at a constant temperature of 250 °C.
In stereolithography, it is not recommended to use TPU for small, thin-layer models or for models that are particularly sensitive to expansion. When configuring the 3D model, it is recommended that the models have the final shape and are positioned close to the print bed, but no flatter than 20 °C. Thinner and taller parts are more difficult to print, although additional supports can always be used to ensure optimal results. Because it is a flexible material, it is very susceptible to causing clogs in the nozzle, leading to printing problems on parts. Filament manufacturers often use the Z-hop function to avoid stresses. This means that instead of creating the next layer horizontally, the extruder rises a few inches and moves to start the next layer, ensuring that no material is left between the part and the nozzle.
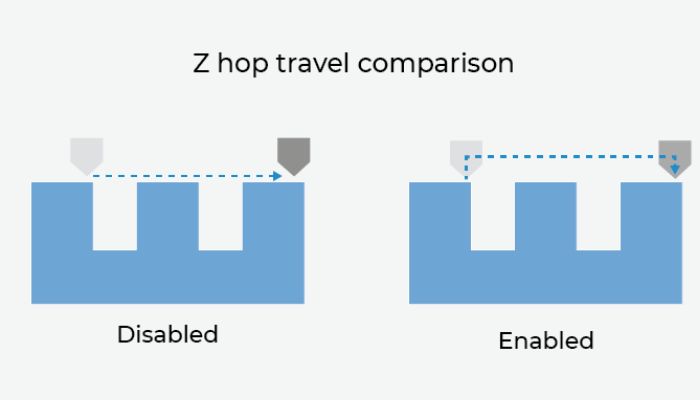
Photo Credits: BCN3D
In addition, it is important to note that each machine and filament is different. Therefore, it is recommended to perform tests to determine the optimal shrinkage value. It should also be noted that this value may vary between different TPU filaments. TPU does not necessarily require post-treatment, but certain techniques can be performed to improve its properties or aesthetic appearance. A common option is a polishing treatment to smooth the surface and remove layer marks, which can improve the final appearance of the printed object. A layer of paint or varnish can also be applied to improve resistance to water, dust and dirt.
Applications for TPU
In the additive manufacturing industry, this material opens up a world of possibilities for different markets. In the footwear sector, elastic soles can be produced, in the medical sector orthopedic models. For the aerospace sector, instruments or sensors are developed, and in the automotive sector, tires and shock absorbers are produced. It can also be found in sports, in the production of protectors in fitness equipment.
TPU is ideal for end-use parts, functional prototypes, concept models and custom components. This type of material is used, for example, in the production of cell phone cases, as it protects the device from impacts and breakage.

The cohesion of the coatings achieves excellent mechanical homogeneity (photo credits: The Lubrizol Corporation)
Main Manufacturers and Price
There are many major companies who offer TPU for 3D printing to enable users to make flexible parts. UltiMaker has a filament called TPU 95A that is compatible with its Ultimaker S5, Ultimaker 3, Ultimaker 2+ and the manufacturer’s newest printer, the UltiMaker S7 3D printers. According to the company, the material supports up to 580% elongation at break. In addition, the filament is available in 4 different colors.
Another major company is Formlabs, which last year introduced its so-called “Elastic Resin” for SLA technology. This resin has a Shore Hardness of 50A, as well as high elongation and energy return. “Shore” refers to the hardness of the material used, or in other words, how resistant a material is to indentation. Lower numbers mean less resistance and softer materials. The elasticity and strength of this material allows it to be used in multiple cycles.
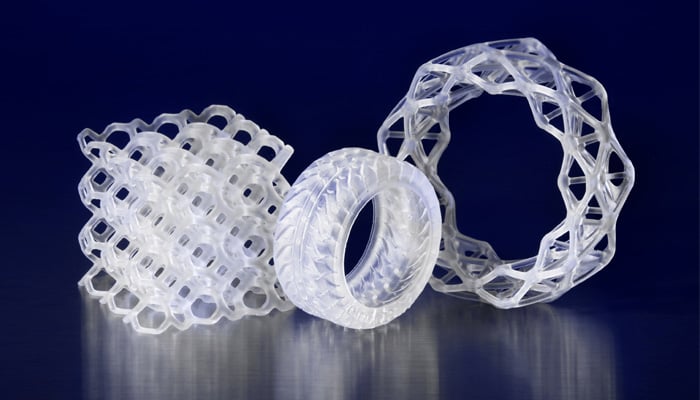

Photo Credits: Formlabs
However, there are other companies that are mainly dedicated to the development of these materials, such as Recreus. This company stands out for the variety of 3D printing filaments it currently offers. In particular, the renowned FilaFlex filament was born from the need to innovate and break the boundaries of 3D printing. Ignacio Garcia, CEO of Recreus, said, “3D printing technology in itself was already innovative, and together with the flexibility of the material to produce flexible parts, such as sneakers, the potential of additive manufacturing and FilaFlex became clear.” Also offering the material in powder form are other companies such as BASF. They have a range of TPU powders under the Ultrasint® name, and their TPU01, for example, is designed specifically for HP’s Multi Jet Fusion 5200 series printers. The price of TPU filament is around $30-40 per kilogram.
Do you use TPU? Let us know in a comment below or on our LinkedIn, Facebook, and Twitter pages! Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter here, the latest 3D printing news straight to your inbox! You can also find all our videos on our YouTube channel.







Probably better to compare TPU elastic properties to DLP PU crosslinked polymer. For 3D printing elastic footwear DLP PU is the industry standard. At LuxCreo, we provide elastic materials that deliver higher energy return and fatigue strength at scale. See ASICS Actibreeze 3D printed sandal . This product could not be realized with TPU (thermoplastic polyurethane) powder or filament.