Researchers Develop Robotic Hand That Can Lift 1000X its Weight
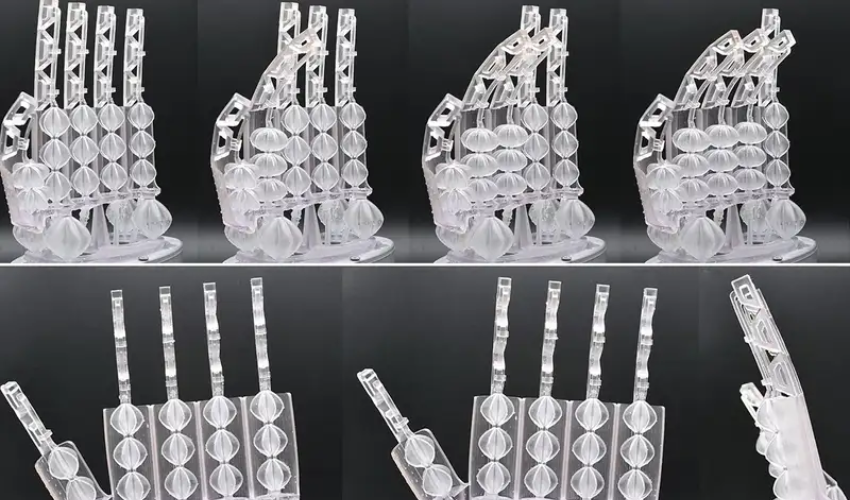
We already knew that ants are capable of carrying 100 times their own body weight. But what if we told you that researchers have succeeded in developing a robotic hand that can carry 1000 times its own weight thanks to additive manufacturing? Well now, this is a reality thanks to Italian researchers at the Italian Institute of Technology (IIT). They have succeeded in producing a robotic hand that while weighing only a total of 8 grams, can lift 8 kilograms of weight and even perform human-like hand movements with muscles. The additive research project was christened GRACE and works by exerting pressure on different actuator membranes so that the robotic hand can perform movements.
Specifically, GRACE is what is known as an actuator. That means it is capable of transforming energy and signals into movements and thus executing commands such as lifting things. The robotic hand working as artificial muscles thus represents a project that may lead to assistance by robots in various areas of society in the future. De Pascali, research member, describes the starting point of this project as follows: “We started from the traditional artificial muscle and developed a new class of artificial muscles made of a single monolithic component.”
Using 3D Printing for the Robotic Hand
Of course, it is not completely novel for robots to be designed with artificial muscles, but what is new with the GRACE actuators is the fact that their membrane contains folds. These folds are largely responsible for the enormous strength as well as flexibility of the artificial muscles, which can be moved like human muscles. The membrane, on the other hand, is manufactured by additive manufacturing and uses flexible resin for this purpose. Similar to a human muscle, it can stretch to a certain extent and then contract again. Previously, according to the research team, stiff resins had been used, but their limited range of motion did not compare with the flexible resin now used.
The starting point for the membrane of the GRACE actuators is a mathematical model developed by the researchers. Depending on the exact model and manufacturing process of the actuator, the material used for it and its width may also differ, which in turn has implications for the gripping force of the robots. In the course of the research in Italy, the research team formed a total of 18 actuators with different sizes into a robotic hand including wrist. Depending on which and how many actuators are combined, the muscle strength and also the imitation on different body parts can thus be influenced. This is an exciting project that has also met with great approval in Great Britain. Jonathan Aitken from the University of Sheffield concluded, “The design of the GRACE is interesting and novel, providing easy antagonistic operation by design.”
What do you think about the robotic hand that allows human-like movements? Let us know in a comment below or on our LinkedIn, Facebook, and Twitter pages! Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter here, the latest 3D printing news straight to your inbox! You can also find all our videos on our YouTube channel.
*Cover Photo Credits: IIT






