Reverse Engineering and 3D Printing: All You Need to Know
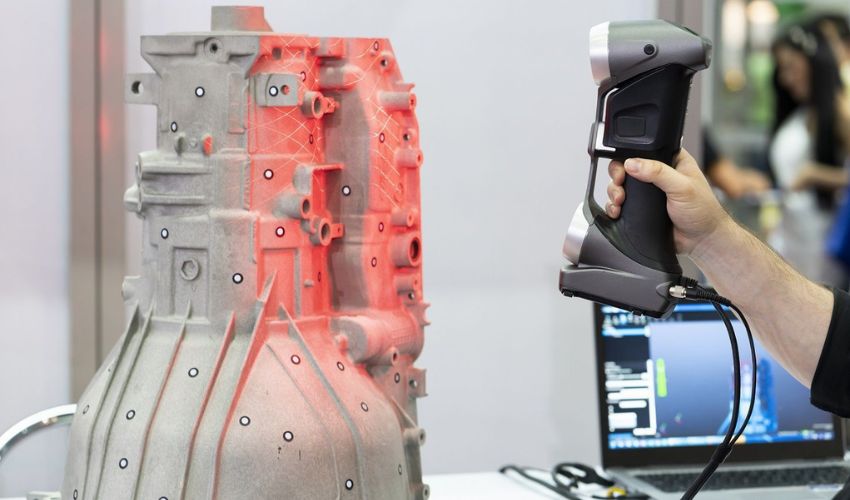

Reverse engineering is a method of analyzing a finished product to understand its design and manufacture. By deciphering the structure and composition of an object, this technique offers the possibility of reproducing it, improving it or drawing inspiration from it for new creations. While it can also be applied to software and other technical fields, we will concentrate here on its use in mechanical engineering.
Combined with 3D printing, reverse engineering becomes a powerful tool, transforming many industries. This combination makes it possible to recreate, optimize and innovate around parts with unprecedented ease and precision. As 3D scanning and additive manufacturing technologies continue to advance, this alliance paves the way for ever more efficient, functional and sustainable solutions. Let’s find out how this technological synergy works, what it can be used for and the benefits.
The reverse engineering process (photo credits: 3dcaptura.cz)
Reverse Engineering: A Multi-Stage Method
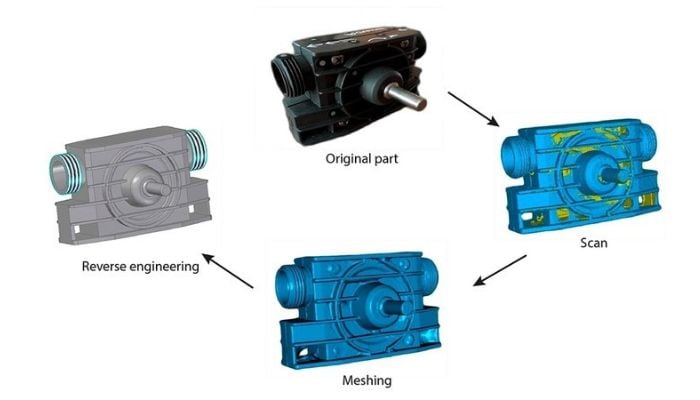
Reverse engineering begins with the digitization of a physical object. Technologies such as laser scanning, computed tomography (CT scanning) or photogrammetry capture the object’s details in the form of a point cloud. This data is then processed in 3D modeling software to generate a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) model.
This digital model can then be analyzed, modified and optimized before being used to produce a new part. In the case of 3D printing, the CAD file is sent to a 3D printer, which materializes the object with impressive precision.
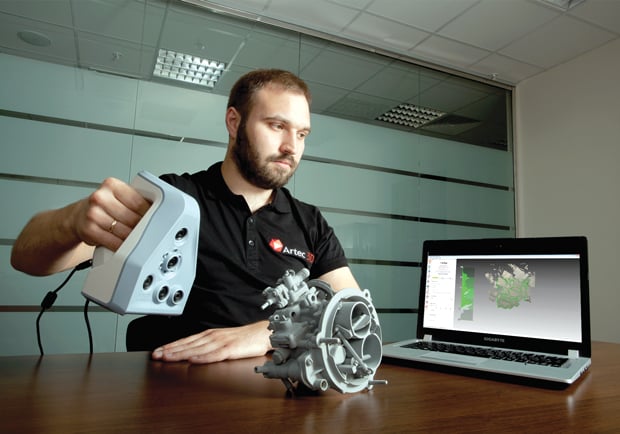

3D scanning simplifies reverse engineering (photo credits: Artec3D)
Software expertise plays a key role in this process. Specific tools not only enable us to reconstruct missing parts of a damaged part, but also to automatically model complex designs and analyze object dimensions and surfaces. Among the most widely used software are: Geomagic, Design X, Catia, Creo, Mesh2Surface and Artec Studio Fusion 360.
Why Opt for Reverse Engineering?
The benefits of reverse engineering are numerous, especially for manufacturers:
- Product development: customizing or improving existing parts to create higher-performance products.
- Optimization: parts can be lightened, strengthened or made more durable, helping to reduce production costs.
- Reproduction of unobtainable parts: in the absence of technical drawings or spare parts available on the market, reverse engineering is often the only solution.
- Innovation: analyzing an existing product often inspires the creation of new solutions.
- Digital twins: precise digital models, used for predictive maintenance or simulations, are based on reverse engineering.
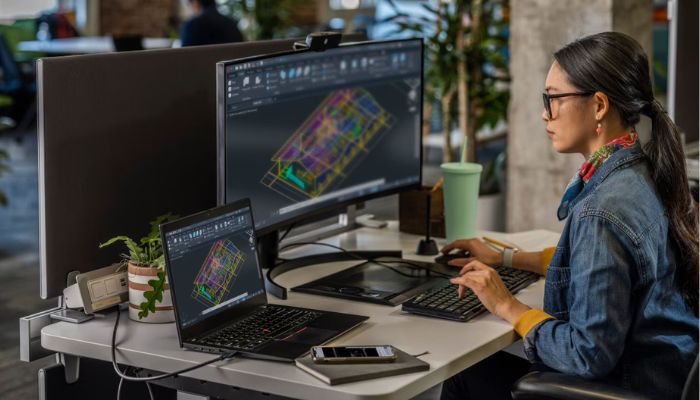

CAD software is used to draw reverse-engineered parts (photo credits: Autodesk)
The Role of 3D Printing in Reverse Engineering
By combining with 3D printing, the possibilities expand considerably. The design freedom offered by additive manufacturing makes it possible to recreate complex shapes or unusual geometries that would otherwise be impossible or too costly to produce.
3D printing often becomes an ally when it comes to reproducing spare parts that can no longer be purchased. Recreating these parts with other production techniques or repurchasing the entire damaged or malfunctioning product would be much more expensive. This is particularly visible when the pieces that you want to reproduce are small or contain fine details that reproducing, for example, with injection molding would be too expensive in terms of time and costs.
Furthermore, when we consider the need for manufacturers to test numerous iterations before arriving at the finished product, we understand why the rapid prototyping and fast iteration capabilities offered by additive manufacturing are a huge advantage.

3D printing combined with reverse engineering is often used to reproduce damaged parts that are no longer on the market (photo credits: Formlabs)
In terms of technologies, there is no real preferred technology when it comes to combining additive manufacturing and reverse engineering. However, we can note that generally the most used technologies in projects of this type are SLA for polymer components and LPBF for metal components, due to the ability of these technologies to guarantee more precise and accurate details. That said, the technologies and materials used mainly depend on the final application.
Applications
But what are some of the concrete applications in which reverse engineering and 3D printing are used together? Besides the production of parts for the manufacturing industry, one of the sectors that regularly makes use of these two techniques is the automotive industry. For example, they can be used for the restoration of historic vehicles. Namely the reconstruction of vintage car parts using reverse engineering and 3D printing has made it possible to keep historic vehicles alive without damaging their original integrity.
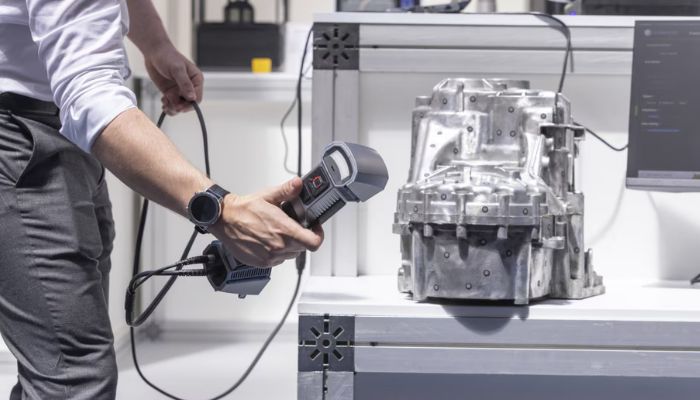

Reverse engineering of automotive parts aids maintenance and optimization of old or vintage vehicles (photo credits: Mihajlo Maricic)
Furthermore, they can be used for optimizing the performance, composition and weight of parts. This is where the aerospace sector in particular benefits from the combination of reverse engineering and 3D printing. Some examples of applications are the production of aircraft components to be added, improved, or repaired, or the creation of new equipment.
Finally, we find not a few applications of these two technologies in the fields of architecture and art: cultural heritage preservation projects have benefited from reverse engineering and 3D printing to reconstruct damaged parts of historic buildings and monuments or to reproduce them at other sites. This approach has enabled the preservation of the architectural and historical integrity of places, but also the reproduction of important works in different locations around the world, where transportation was not possible, to enable as many people as possible to enjoy them.
What opportunities do you see in the synergy between reverse engineering and 3D printing? Let us know in a comment below or on our Linkedin, Facebook, and Twitter pages! Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter here, the latest 3D printing news straight to your inbox! You can also find all our videos on our YouTube channel.






