All You Need to Know About PESU in 3D Printing

Belonging to the sulfone family, polyethersulfone, or PESU, is a high performance material which has a unique thermal profile in the world of thermoplastics. Very heat resistant, it is an amorphous polymer which, while displaying interesting properties for many industries, is still little known in the world of additive manufacturing. PESU can be bought in the form of filaments, powders and injection grade granules. Injection grade granules tend to possess higher levels of material purity and thus make the printing of functional parts in the raw form of PESU possible.
Notably, this makes the same standards and certifications as the material used in injection attainable, and therefore also makes it possible to offer a high performance material ideal for manufacturers. A noteworthy player in this domain is French company Pollen AM, a pioneer in using PESU pellets for additive manufacturing. Their extensive research has provided valuable insights into the material’s characteristics. But what exactly are those characteristics and what makes PESU such an attractive material for the AM industry?
Chemical structure of polyethersulfone (PESU).
Production and Characteristics of PESU
Polyethersulfone is especially renowned for its thermal properties: It can in fact withstand very high temperatures (up to 220°C or 429°F), even in a liquid and vapor environment up to 170°C (338°F). It exhibits fire / smoke resistant characteristics making it a material of choice for the aerospace, rail and automotive industries. To give you an idea, the material begins to degrade above 400°C (752°F) with a combustion that starts between 475 and 575°C (887°F and 1067°F). In addition to this unique thermal profile, PESU is food safe, can withstand very high loads and exhibits good electrical insulation and dielectric properties.
PESU is typically produced through a step-growth polymerization process, where monomers containing ether and sulfone functional groups react to form long polymer chains. The main monomers used in PESU synthesis are 4,4′-dihydroxybiphenyl sulfone (BPS) and 4,4′-difluorodiphenyl sulfone (DFDPS), which are reacted in the presence of a catalyst and solvent. The polymerization process results in a high molecular weight polymer with a linear structure.
Polyethersulfone (PESU) is a remarkable material with a range of exceptional characteristics. It exhibits exceptional thermal stability as previously mentioned, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. PESU also boasts excellent chemical resistance, making it resilient to various acids, bases, and organic solvents, even under harsh chemical exposure. Its high mechanical strength and stiffness make it suitable for applications requiring structural integrity and load-bearing capabilities. Additionally, PESU maintains its dimensional stability even under extreme conditions, including high temperatures and varying environments.
It exhibits good electrical insulation properties, making it a reliable choice for electrical and electronic components. Being inherently flame-resistant, PESU complies with various fire safety standards without the need for additional flame-retardant additives. Its excellent optical clarity allows it to be used in applications where transparency is required. To some extent, PESU is biocompatible and has been employed in certain medical and healthcare applications. Overall, PESU’s exceptional properties make it valuable across various industries.

PESU’s high mechanical strength and stiffness make it suitable for applications requiring structural integrity and load-bearing capabilities (Photo credits: Gerdau Graphene)
3D Printing with PESU
PESU is an amorphous material, and therefore has a disordered molecular structure. Unlike a semi-crystalline material, it is comparably easy to shape because it undergoes less contraction and expansion effects at temperature. Its melting point is between 340 and 390°C (644 and 734°F). These two characteristics make it, a priori, an ideal material for additive manufacturing.
PESU allows manufacturers to 3D print complex parts, and the fact that it is resistant to heat, fire and smoke is especially a benefit in certain industries. If we compare it to the PEI (for which the best-known brand is ULTEM) for example, now available in the form of filaments, PESU not only has better characteristics but is less expensive. In addition, polyethersulfone has a significantly lower moisture uptake, and therefore represents an alternative to be seriously considered. That being said, it can be hard to adapt the material to FDM printing specifically, and though it is currently available through some material manufacturers, it should be noted that to turn it into a filament often causes it to lose characteristics that make it appealing in the first place, though there are companies working to overcome this obstacle.
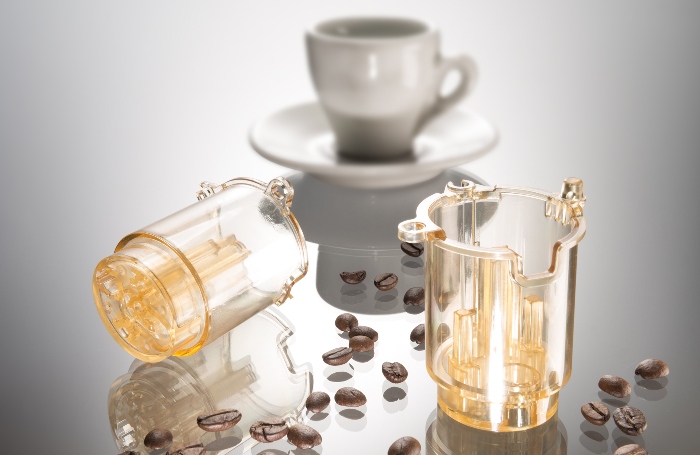

Household appliance manufacturer De’Longhi uses polyethersulfone (PESU) by BASF for upper piston of brewing unit in coffee machine (Photo Credit: BASF)
Applications of Polyethersulfone
As you can guess, thanks to its exceptional thermal characteristics, 3D printed PESU finds applications in a wide range of industries. It is popular with the transport sector, not only for aerospace and rail, but also automotive, electronics, medical, and consumer goods applications. It is commonly used in the production of aircraft components, automotive parts, electrical connectors, filtration membranes, and medical devices. Its versatility, strength, and resistance to high temperatures and chemicals make PESU a valuable material in demanding engineering applications. As it is resistant to fluids, greases and petrol, it is suitable for the manufacture of things like probes for checking oil levels. PESU is also used to design personal protective equipment.
Finally, PESU is often used to replace the family of polyamides and more particularly polycarbonate. It offers good transparency, and is food safe and sterilizable. Note, however, that the PESU is not flexible. Though not currently a widely manufactured material for 3D printing, there are several companies that offer it. Due to its impressive qualities, it does seem likely that in the near future it will be used more as the aerospace and the automotive industries, especially, start to move more into using 3D printing in the production of end use parts.

Reinforced PESU resin is becoming a popular choice for automotive components, gradually replacing traditional metal and thermoset materials. (Photo credits: SpecialChem 2023)
Manufacturers and Price
Several manufacturers produce PESU, offering different grades and formulations tailored to various industrial applications. Some well-known manufacturers of PESU include Pollen AM, Solvay, BASF, Victrex, Ensinger, and SABIC. These companies have a reputation for producing high-quality engineering thermoplastics and are likely to offer PESU in their product portfolios. Regarding pricing, the cost of PESU can vary depending on factors such as the grade, quantity purchased, and the supplier. Generally, PESU is considered a higher-priced engineering thermoplastic due to its exceptional properties and performance characteristics. Prices can range from approximately $40 to $100 or more per kilogram, depending on the specific grade and supplier.
It’s essential to note that pricing may change over time due to fluctuations in raw material costs, market demand, and other factors. For the most current and accurate pricing information, it is recommended to contact specific manufacturers or authorized distributors directly. Additionally, it is advisable to compare prices from multiple sources to ensure the best value for the intended application.
Do you use PESU in additive manufacturing? Let us know in a comment below or on our Facebook and Twitter pages! And remember to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter, to get all the latest news in 3D printing sent straight to your inbox!
*Cover photo credits: Medical Plastics News






