Monitoring Food Freshness With 3D Printing and Neural Networks

Can we rely on our five senses to know if fruits and vegetables are fresh or not? In most cases, it is enough to observe, smell or touch the food to realize that we can eat it. In these cases, there is usually not much risk. However, in the food industry, quality standards can be more demanding and ensuring the freshness of fruits and vegetables during transport and storage can become an even greater challenge. As a solution, a recent study from Jiangnan University in China has developed a new system that combines 3D printing with deep convolutional neural networks (DCNN) to monitor the quality and freshness of foods like fruits and vegetables in real time.
Using 3D printing, labels were made with color indicators that detect changes in CO₂ levels that occur during the decomposition of fruits and vegetables. And by means of deep convolutional neural networks, the results displayed by the labels were interpreted. By combining these two technologies, the perfect method for monitoring the freshness of fruits and vegetables was achieved.
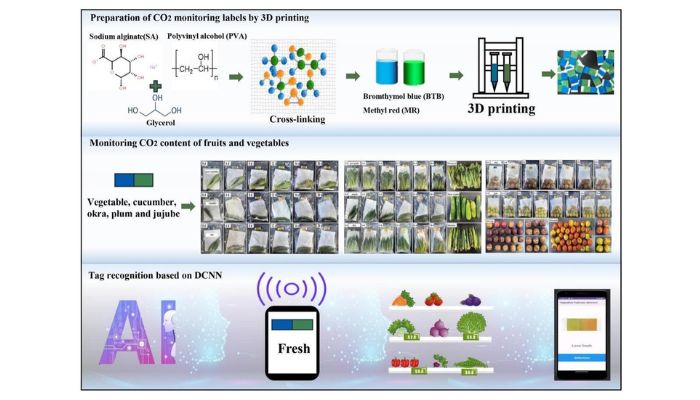
3D printed labels monitor changes in CO₂ levels during storage of vegetables such as green vegetables, cucumbers, okras, plums and jujubes to better understand food freshness (photo credits: Tiantian Tang, Min Zhang, Huijie Jia, Bhesh Bhandari, Zhimei Guo)
How Do 3D Printing and Neural Networks Relate to 3D Printing?
Before going into the details of the study, it is necessary to mention what deep convolutional neural networks (DCNN) are. These are a class of artificial neural networks that are frequently used to analyze different images. Taking advantage of the design flexibility of 3D printing, the labels contain color indicators based on bromothymol in blue and methyl in red. In this way, the labels show the changes in CO₂ levels that occur during the decomposition of fruits and vegetables.
3D printing technology proved to be a versatile solution for the manufacture of these labels, using biocompatible materials such as sodium alginate, starches and polysaccharides, which also makes them safe for food packaging. The study found a direct relationship between label color changes and food freshness. Increased CO₂ in the storage environment was also found to correlate with increased weight loss and decreased product firmness.

Jiangnan University, in China (photo credits: Wuxi China)
As mentioned above, neural networks interpreted the data obtained from the labels. The networks analyzed the label images and classified the food into three categories: fresh, slightly fresh and spoiled. The use of DCNN made it possible to achieve high accuracy in detecting the condition of the products. The study was taken further by developing a mobile application based on this model, which allows scanning the labels and obtaining an immediate diagnosis of the freshness of the food.
The combination of 3D printing with neural networks may open up new opportunities in food supply chain monitoring. Perhaps in the future the method could be expanded to other products such as meat and dairy, integrating additional sensors for temperature and humidity detection. The researchers have even mentioned that incorporating antimicrobial agents into printed labels could help extend the shelf life of foods. Read more about the study HERE.
What do you think about using 3D printing to help monitor food freshness? Let us know in a comment below or on our LinkedIn, Facebook, and Twitter pages! Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter here, the latest 3D printing news straight to your inbox! You can also find all our videos on our YouTube channel.







