Mitsubishi Electric develops a metal additive manufacturing process

Mitsubishi Electric Corporation is a Japanese electrical equipment manufacturer and one of the world’s largest producers of photovoltaic panels. It is also a player in the additive manufacturing market that has already developed a hybrid machine combining metal sintering and milling. The company announces this time a new 3D metal printing technology that it calls ” Dot Forming ” that is to say a method that would form points, inspired by the technology of metal deposition under concentrated energy ( DED in English). The machine developed would combine both laser, CNC and CAM to produce quality parts.
This initiative qualifies Japanese Mitsubishi to our list of metal 3D printer manufacturers, which keeps growing, and for good reason. According to the Wohlers Report 2018 , the 3D metal printing sector has increased by 21% last year and this trend seems to be continuing. Manufacturers benefit from this growth; for this we can look to HP’s recent announcement at IMTS in Chicago, which chose the MIM-inspired powder binding technique for its new HP Metal Jet. The Japanese manufacturer has turned to a method that uses DED technology. Whereby a source of energy is used to melt and fuse materials at the time of deposit.
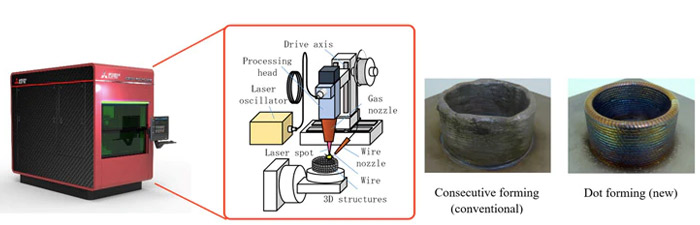
The operation of the Mitsubishi process and printing samples
Mitsubishi Electric’s Dot Forming Technology
The DED process is commonly used to repair and maintain structural parts, but also to create hollow or overhanging shapes. Mitsubishi Electric explains that unlike the DED, its unique technology uses a laser-welding wire. This wire is quit a lot cheaper than when using the conventional powder method. The technology repeats the formation of points by synchronously controlling the pulsed laser irradiation, the wire feed and the shielding gas, as well as the shaping position. With this repetition effect, Mitsubishi Electric claims that the shape accuracy is 60% higher than other metal additive manufacturing processes. As for the oxidation, it’ll be reduced by 20%. Do to the high temperatures are concentrated on a small number of points.
Mitsubishi Electric hopes that its new technology will increase productivity for a wide range of applications. This includes areas such as repairing aircraft and automotive parts, as well as producing near-finished parts. The company presented its machine at the International Machine Tool Exhibition in Tokyo at the beginning of November. The first deliveries will not be made until 2021. In the meantime, find more information in the official press release HERE .

Parts created by Mitsubishi technology
What do you think of the process developed by Mitsubishi Electric? Let us know what you think in a comment below or on our Facebook and Twitter pages! Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter, with all the latest news in 3D printing delivered straight to your inbox!






