Kiri:Moto, The Online Slicer for 3D Printing from Grid.Space
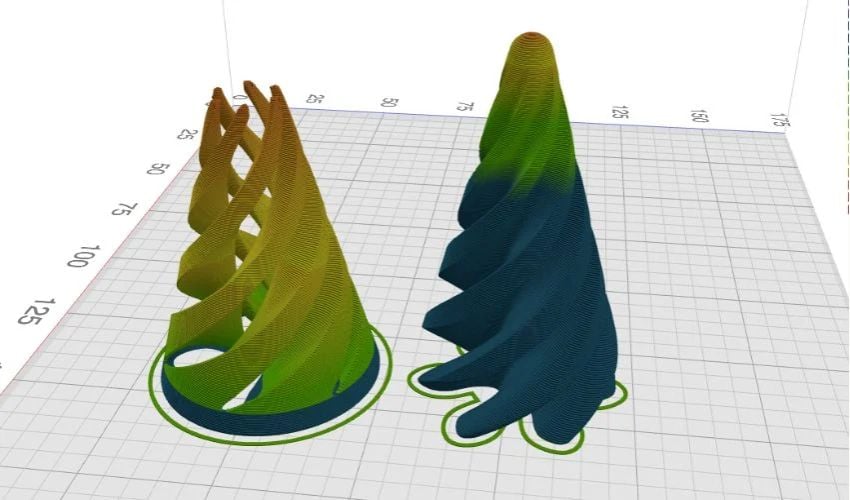
In any 3D printing project, certain steps must be followed, regardless of the type of printing used. We start with 3D modeling, followed by the generation of G-Code using a slicer. Next, the object is printed, and finally, the necessary finishing touches are made in post-processing. Today, we’re going to take a look at the slicer stage by introducing you to a free tool that simplifies this task: Kiri:Moto. Unlike other software, Kiri:Moto does not require any installation, as it is an online application, and stands out for its relatively easy-to-use interface.
Before introducing the application, it is important to remember the essential role of a slicer. A slicer acts as a translator, transforming a digital model into a language that can be understood by the 3D printer. It cuts the model into horizontal layers and generates G-code, a series of precise instructions that the printer follows to build the object layer by layer. But slicers do more than just this simple conversion: they also optimize every aspect of the printing process. They allow you to adjust parameters such as speed, fill rate, supports, and material quantity in order to achieve the best possible result.
The name Kiri:Moto is composed of two words: Kiri, which refers to the word Kiri-e, the Japanese art of paper cutting, and Moto, a short form of “modeling tool” (Credits: NeoTeo).
How Is Kiri:Moto Different from Other Slicers?
As mentioned above, Kiri:Moto is a free slicer that does not require installation, as it is a web application. Developed by Grid.Space, this online solution offers features tailored to FDM and SLA 3D printing processes, as well as other techniques such as CNC milling and laser cutting. Kiri:Moto offers a dedicated interface for each of these processes, allowing it to be used for a variety of needs. In addition to being free, Kiri:Moto is open source software whose code is available on GitHub under an MIT license, allowing anyone to modify it freely. This feature may be of particular interest to users who want to learn Java programming, the language in which Kiri:Moto was developed. This slicer stands out for its ease of use, high level of customization, and cloud integration, making it accessible from any device connected to the Internet. As noted by Grid.Space, Kiri:Moto offers features comparable to those of other popular slicers such as Cura, Simplify3D, and PrusaSlicer.
Kiri:Moto’s Interface
The Kiri:Moto interface has been designed to combine simplicity and efficiency, retaining only the essential features. Upon opening the program, users will find an intuitive and easy-to-navigate environment that will seem familiar to those who have used other slicers. The interface is structured into several sections:
- Work area: this is where 3D models are imported and viewed. Users can manipulate their models by moving and rotating them freely.
- Settings panel: located on the left side of the interface, this panel contains all the settings related to printing, such as layer height, print speed, temperature, infill rate, and support options.
- Tools menu: located on the right side of the interface, this menu manages the workspace, operating mode, and objects. It is divided into three main sections. The first section allows you to select the machine used (FDM, SLA, etc.), configure interface preferences, and import files. The second section offers options for viewing and previewing the 3D model cutout. Finally, the third part of the menu contains rendering settings, part manipulation tools, and the option to select extruders in the interface dedicated to FDM machines.
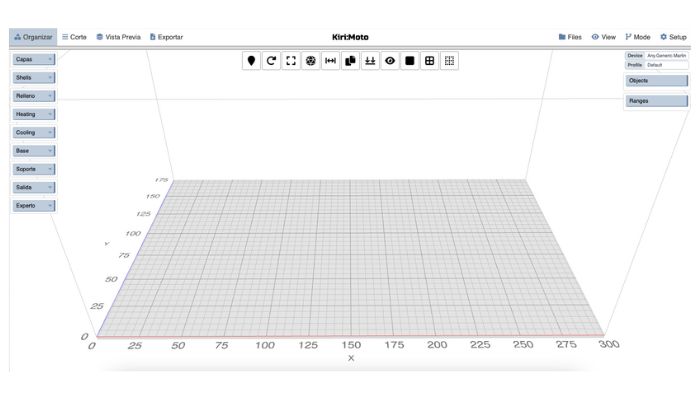
The 4.0 version interface for FDM.
Kiri:Moto offers an almost identical interface for other processes, with the addition of a few options specific to each one. For example, when preparing a file for CNC milling, a new menu appears at the bottom of the screen, allowing you to plan and control the various milling operations.
The Characteristics of Kiri:Moto
An important point to note is that previous versions of Kiri:Moto remain easily accessible via the Grid.Space website. In 2024, they released the new 4.0 version interface, which includes more features for advanced printing. In addition, Kiri:Moto receives regular updates, sometimes several times a week, bringing new features.
Kiri:Moto supports importing STL, OBJ, and 3MF files for 3D parts. In addition, SVG files are automatically converted into 3D models. This diversity of formats allows users to easily manipulate the most common models. Finally, Kiri:Moto can be integrated with other tools such as OnShape and Thingiverse. For OnShape, Kiri:Moto integrates as a web application extension, allowing you to quickly upload parts and generate G-code directly from OnShape, without having to go through an export and import process in the slicer. As for Thingiverse, users can open files directly with Kiri:Moto, making it easy to access Thingiverse models, slice them, and print them without having to download and re-import them into the slicer.
What do you think of Kiri:Moto? Let us know in the comments or on our LinkedIn or Facebook pages! Plus, don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter to get the latest 3D printing news straight to your inbox. You can also find all our videos on our YouTube channel.







