Hiperbaric and Aenium Team Up to Show Benefits of Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) Technology for Additive Manufacturing

Spanish company, Hiperbaric has sealed an Industrial R&D Collaboration Alliance with Aenium, an engineering company specializing in AM technologies. Hiperbaric is a world leader in HPP (high pressure processing), a technology for preserving food and beverages by high hydrostatic pressure (with water). In 2020, they started working with HIP (hot isostatic pressing) in order to become leaders in high pressure technology applied to various sectors, such as AM. Additionally, the company has announced the inauguration of its HIP Innovation Center where companies from across the world, including those in the 3D printing sector, can come to test their components using HIP processes. The use of HIP processes in AM promises to create components with even higher quality standards, making them ideal for sectors such as aerospace, energy, automotive, oil and gas, industry and medical implants.
The agreement between the companies signals their combined commitment to develop and improve industrial metal components, notably showing the value of combining HIP and AM. Andrés Hernando, CEO of Hiperbaric notes, “The agreement with Aenium supports how Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) post-processing technology is combined with Additive Manufacturing techniques to achieve parts that require excellent mechanical properties.” As HIP processes are ideal for optimizing material properties, especially in metals, and in producing parts with greater reliability, it is no wonder the companies saw the benefits of combining the two technologies. Both Hiperbaric and Aenium have affirmed their commitment to jointly respond to challenges and needs in AM and HIP, working to achieve faster and more economical post-processing cycles.
A component being printed using Aenium’s equipment.
What is HIP?
HIP is essentially a manufacturing process that, as the name implies, involves applying high levels of pressure and temperature to parts and components. The benefit of using this particular technology is that it helps to improve the mechanical properties of metallic or ceramic parts and components. In essence, the process helps to densify the structure, allowing the material to develop better mechanical properties in regards to fatigue life, resilience or ductility (when a solid material stretches under tensile strain). All in all, this process means that there will be less variability and better consistency with parts, making components more reliable. This is especially valuable as you can imagine in a number of sectors, including AM where the process can be used to optimize metal powders.
Though perhaps not as well-known in the AM world, HIP processes can provide significant benefits to AM users. Notably, the combined use of these technologies has proven to enable more efficient designs. This is because HIP works well with AM, resolving certain challenges in 3D printing such as allowing for large-scale volume production. HIP technology improves the properties of metal parts made using AM, making it especially important for AM companies that work with industries such as aerospace wherein it is critical that final use parts be reliably consistent. The collaboration is expected to be a boost in the market for additive manufacturing of metal components as it will rise to address challenges that already exist in both industries. Hernando stresses “The way to overcome these challenges is to build strong partnerships between different solution providers, such as with Aenium and Hiperbaric”
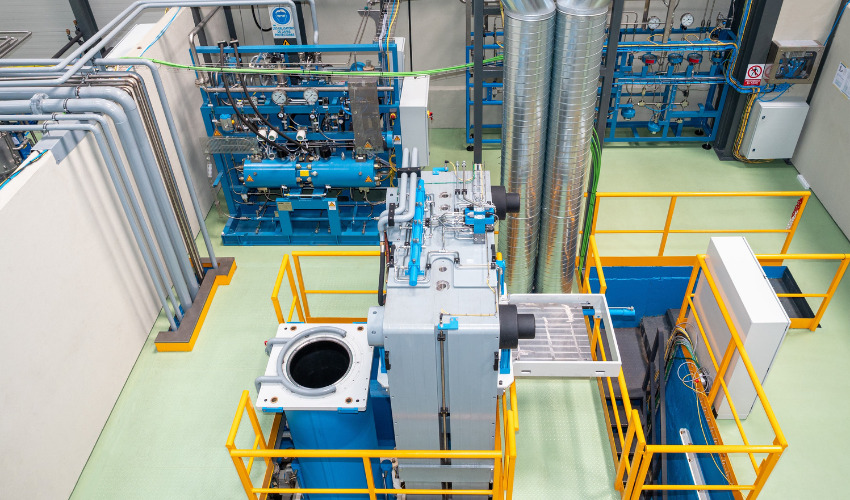
Hiperbaric’s HIP Innovation Center
Of course, the partnership with Aenium is not Hiperbaric’s only foray into the AM sector. Hiperbaric has also recently opened the HIP Innovation Center in Spain. This center, the first of its kind in Spain, will allow companies from all over the world to get advice and test components to validate HIP processes. The HIP Innovation Center is open to experimentation, testing, validation of metal and ceramic parts, manufactured by any technique and for any type of sector that needs the advantages that HIP provides. Though as the partnership with Aenium suggests, one of the sectors that will most benefit from the technology is additive manufacturing.
The HIP Innovation Center has a 38 HIP press which is capable of 2000 bar and 1400 °C (30,000 psi and 1675 °K) through an inert atmosphere (in this case using argon gas, noted for its non-reactivity). Additionally, the press is equipped with a Ø380 mm x 1200 mm (Ø14.5 inches x 47 inches) molybdenum furnace and Fast Cooling technology. The benefit of Fast Cooling technology is that it will cool parts in a much faster and more uniform way, allowing users to increase productivity and enhance the material properties of said components.
Beyond the equipment, the Center also boasts a large team of industrial engineers who are experts in materials and mechanical characterization of complex structural parts and assemblies. They will be able to answer questions for those who may be less familiar with the processes to help find optimal solutions to any technical challenges. Though open to all industries, the Center will be an invaluable asset to AM companies hoping to see firsthand the benefits of using these processes. They will be able to test materials as well as see how presses improve the quality of components, with Hiperbaric highlighting especially that the center can be used to optimize parameters to get the most out of metal components. If you are interested in learning more about Hiperbaric, you can check out their website HERE.
What do you think of the partnership between Hiperbaric and Aenium? Let us know in a comment below or on our Linkedin, Facebook and Twitter pages! Sign up for our free weekly Newsletter here, the latest 3D printing news straight to your inbox! You can also find all our videos on our YouTube channel.
*All Image Credits: Hiperbaric






