How to Choose a Resin 3D Printer? Experts Give Their Advice!

In 1986, Charles Hull filed one of the first commercial patents in the 3D printing sector for stereolithography (SLA), a process which uses a laser to polymerize photosensitive resins, layer by layer. Since its invention, other photopolymerization methods have been developed including DLP and LCD which, instead of using a laser that will act point by point, use a screen to cure the entire layer of resin in a single pass. Though each method has its own specific characteristics, it should be noted that in general resin additive manufacturing is often known for its precision and the fineness of details that can be obtained – especially compared to FDM. But how to choose a resin 3D printer? Which process is the best fit for varied needs? We interviewed three experts in the sector to find out more!
Our first expect is Bo Pang, a 3D printing product manager at SHINING 3D, a leading provider of imaging and resin 3D printer solutions. He has been working in the industry for 8 years, mostly in SHINING’s R&D department, and focuses on resin 3D printing. Next, Robin Brockötter is the 3D printing supply chain manager for Europe and the UK at Hubs, the world’s largest peer-to-peer network of 3D printing services. He has been with the company for 8 years. Finally, our last expert is Julien Montenero, a facial, dental and maxillofacial prosthesis technician who has been using resin technology for different applications for 15 years.
- Bo Pang
- Robin Brockötter
- Julien Montenero
Why Turn to Resin 3D Printing?
One of the main advantages of resin additive manufacturing is its ability to produce very detailed parts with high precision. However, among the processes, this still differs. Robin Brockötter explained what users could expect: “The specs of the different resin printers differ from one brand to another. For example, when it comes to LCD printers, which are generally more affordable than desktop SLA machines, the resolution of the screen determines the precision of the print. The layer thickness is usually a setting that can be adjusted. This varies anywhere between 25 microns to 200 microns per layer (draft mode on Formlabs for example). Meanwhile, laser SLA printers generally have the highest precision.”
Furthermore, resin 3D printing is particularly suited for obtaining accurate models. For Julien Montenero, it is a process that allows him to faithfully reproduce the models he needs: “The process offers an unprecedented quality of execution. Beyond this aspect, it allows us to validate and execute our work in a perennial and faithful way. Thanks to 3D printing, we can set up and reproduce our aesthetic and functional plans.”
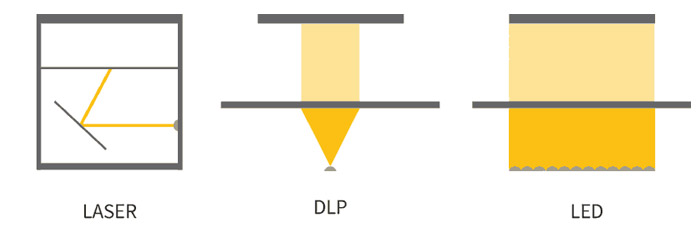
The different 3D resin printing processes
Another important aspect to consider when choosing resin 3D printing is the materials. Though the range is not as broad as with FDM printing, material improvements are rapidly increasing the number of applications available, including for desktop resin 3D printing. Bo Pang puts it this way: “Benefitting from the many material improvements in resin 3D printing, more and more engineers are starting to deploy resin 3D printer on their desk. Indeed, the technology is ideal for making functional prototypes. Instead of outsourcing the prototyping and waiting for weeks, a resin 3D printer can get most the job done within hours. Furthermore, there are many high-performance engineering materials available with properties comparable to ABS, PC or Silicon Rubber.”
Resin 3D Printing Applications
Additive manufacturing is used in many sectors of activity and some processes are more adapted to certain types of applications. This is the case with resin 3D printing, which is ideal for the creation of figurines, models for architects, or even for the medical sector, especially dental. Bo from Shining 3D expands: “The most suitable application for resin 3D printing is dental. Almost all the dental application can benefit from resin 3D printing, such as orthodontics, restorations and implants. The top orthodontics manufacturers print over 700,000 models daily.” This view is shared by Julien, who very quickly adopted resin machines to manufacture prototypes of crowns and bridges, but also prototypes of breast prostheses, noses, ears, etc. The biocompatibility of certain resins is particularly appreciated by health professionals.
However that is not all resin 3D printing is also popular with the jewelry industry, which uses it to produce precise molds that will be used for lost-wax casting. Pang noted, “Jewelry is also an important application for resin 3D printing. DLP and LCD technologies can print ultra-high details and features, even smaller than a hair. A lot of jewelry designer using 3D printer and wax resin, to make their work in house.”
Resin 3D printing can be used for a wide variety of applications (photo credits: Shining 3D)
For Robin as well, resin 3D printing can be used for a wide array of applications, mentioning as well the importance that material choice can have on the end part: “Resin printing is highly precise and is particularly excellent for visual end-uses. Resins are available in a wide range and optimized for diverse applications thanks to unique properties, such as flexibility, toughness, and castability. Different types of clear resins can be polished to a glass-like finish. On the other hand, generic white, grey and black resins are preferred for prototyping parts right before they are validated for injection molding.”
Challenges to Overcome
That being said, getting into resin 3D printing is not easy – a beginner will tend to choose FDM as a starting point. Indeed, you have to master a certain number of parameters such as the exposure time or the speed of the plate to obtain successful prints. Bo Pang mentions that there are a lot of different things to consider including print size, accuracy, speed, material, nesting, slicing software and, of course, post-processing. He especially notes the importance especially of design and post-processing: “Nesting and slicing is the first step for 3D printing, a good software can make the pre-processing quick and easy. Most of the 3D printer company provide free trial to the software, make sure you like the software before you buy. Furthermore, resin 3D printing requires wash and post-curing. A compatible curing station is essential, it can strengthen the part by 30%~50%. A good washing station can save a lot of labor cost, make the whole process simple and easy.”
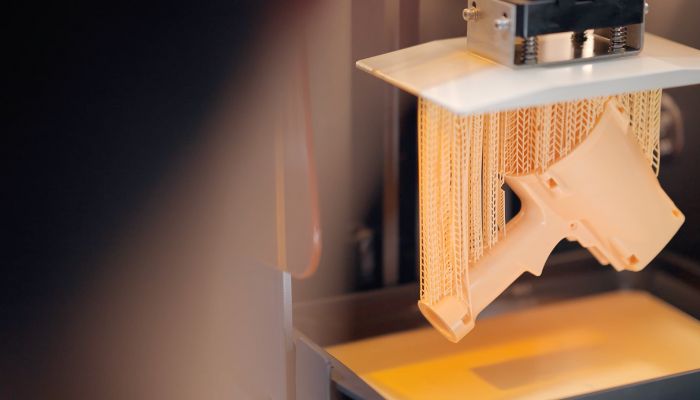
Another challenge of resin processes is the unavoidable use of printing supports. During the printing process, these supports hold the part on the plate and must be removed when finished. It is necessary to go through post-processing steps – washing the part to remove the excess resin, annealing it if necessary to give it all its properties. However, this challenge can also be mitigated with the help of design knowledge. Robin explained how Hubs helps customers looking to create parts with resin 3D printing: “We also provide design recommendations that improve various facets, such as printability, part strength, material consumption and more. All this is, of course, done while accounting for the limitations of the SLA process. This includes the little things, such as optimizing support structures required to print the parts or the minimal wall-thickness required for a successful print. For example, if your design has internal features, we want to make sure our production partners orientate the part in a way that minimizes the need for support structures.”
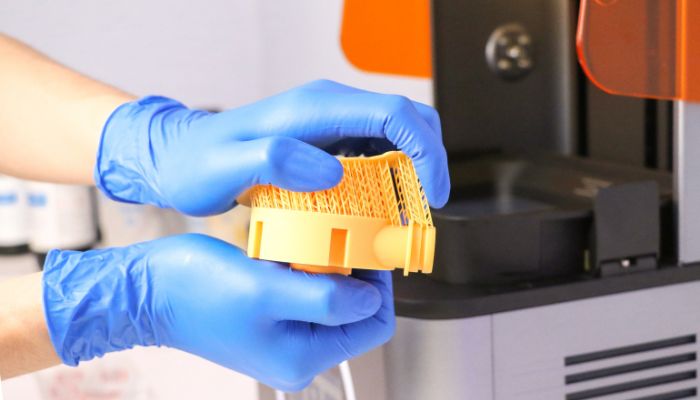

Resin 3D printed parts must be printed with parts which then need to be removed (photo credits: Shining 3D)
How to Choose a Resin 3D Printer?
The starting point for choosing a resin 3D printer is to identify its applications: what will you print? How often? What properties do you want to give to the final part? These questions are essential for refining your needs and choosing the right solution. Robin Brockötter further explains, “Similar to what resin we would recommend, it’s important to know the intended application when choosing a resin printer. Are you working for a company that will run the machine 24-7 for customized dental mouthguards or are you a hobbyist that prints their own designs every now and then? These considerations will all impact which resin 3D printer you choose to buy.”
Once this reflection is underway, our experts advise testing different machines, going through a service provider, visiting fablabs, etc. Julien explains: “It is necessary to carry out a study of needs and costs in relation to one’s activity in order to be able to meet our expectations as accurately and quickly as possible. It is very important to do a lot of tests before making a real choice, thanks to the many communities currently available on the networks, finding a provider in all 3D printing solutions is accessible to all. By testing, the comparison of results is easier as well as the choice of equipment, whether it is the printer but also the post-processing material.”
Bo Pang also notes the importance of support when choosing a 3D printer. He concludes, “3D printing industry is still at its early stage, you might meet different questions when using the product. 3D printer is not like consumer electronics, it has its own learning curve. We should always choose the product from the company, which can provide reliable product, appropriate training and good service.”

Photo Credits: Shining 3D
Do you use resin 3D printing? Which resin 3D printer would you choose? Let us know in a comment below or on our LinkedIn, Facebook, and Twitter pages! Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter here, the latest 3D printing news straight to your inbox! You can also find all our videos on our YouTube channel.
*Cover Photo Credits : 3Dnatives









