What are the best 3D startups of 2020?

Startups are young companies with innovative business ideas. They serve as drivers and integrators of digitalization and promote competitiveness and innovation. As the 3D printing market still has a great potential for growth, startups are of great importance in the development of the industry. For this reason, we have been introducing you to a new startup in additive manufacturing every month. The end of the year is approaching so we want to elect the most innovative 3D startup of 2020. To do this, we are launching a competition: until January 4th, you can vote HERE for the 3D startup that you think is worthy of the title of Startup of the Year. We will announce the winner on January 5th! Like every year, you can find a summary of the 12 startups below!
January: AdditiveLab
Belgian startup AdditiveLab offers simulation software for additive manufacturing. This means that the software allows customers to create specific models for AM process simulation. This gives customers insights into expected material and machine costs and the length of the manufacturing process. This is especially beneficial for metal 3D printing, as metals are more expensive to purchase and produce than polymers. The versions of the software are available: AdditiveLab RESEARCH and AdditiveLab LITE. AdditiveLab RESEARCH is aimed at advanced simulation engineers and provides access to in-depth simulation capabilities. AdditiveLab LITE is particularly targeted at engineers without simulation experience due to its ease of use and is also the more cost-effective option.
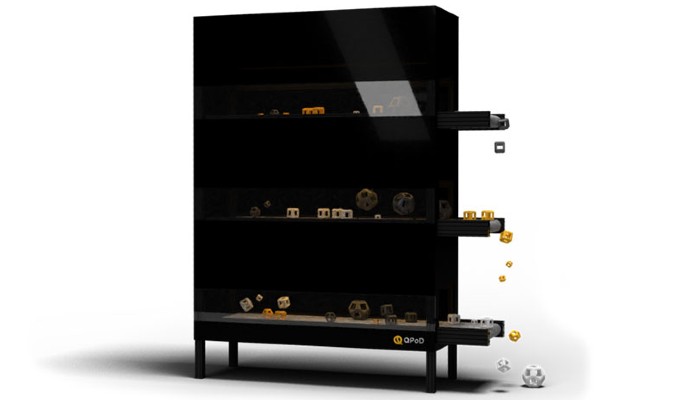
February: 3DQue Systems
The Canadian-based startup 3DQue Systems has developed a system that enables permanent production. This consists of the QPod 3D printer and the accompanying QSuite software. The solution enables in-house production of plastic parts with little or no maintenance. For example, it is said to allow on-demand production of parts made from PLA, ABS, TPU, PETG and Nylon. According to the manufacturer, lead times can be reduced by 95% (from months to hours) and inventories can be reduced by 85%, ultimately reducing costs. With their solution, they aim to show that FDM printers are very much capable of manufacturing beyond prototypes, making them our Startup of the Month for February 2020.

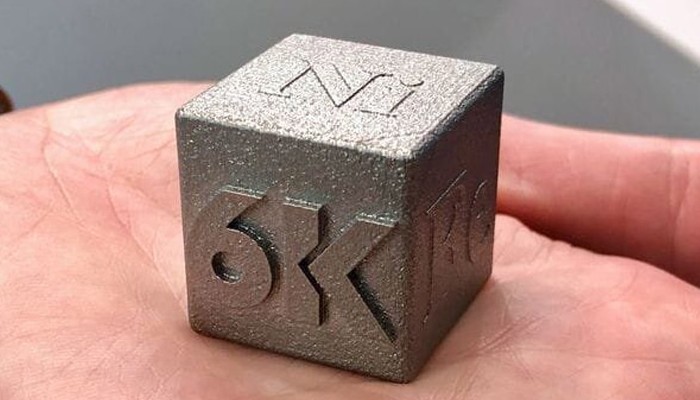
March: 6K
6K is a young American company specializing in the production of materials in powder form for additive manufacturing and other production processes. The company has developed its microwave plasma system, called UniMelt, for the production of materials in powder form. Unimelt converts a wide range of materials, including ceramics, metals and plastics, into high-quality powders at 6,000 degrees. This allows unique alloys to be created, for example. In addition, the solution is convincing in the aspect of sustainability: even certified machine scrap, used powder and other sources of potential raw materials can be converted back into quality powder.

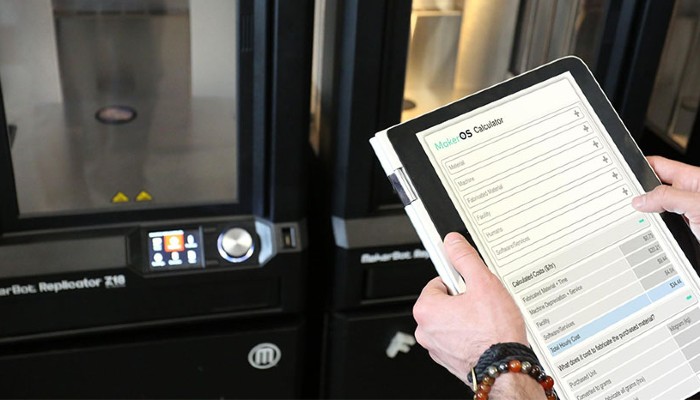
April: MakerOS
Our Startup of the Month in April 2020 was MakerOS. MakerOS has developed online software for companies that offer 3D printing and other digital manufacturing services. Essentially, the MakerOS platform allows you to communicate, submit projects, view updates, and access files and invoices in one central cloud-based solution. As a result, it is designed to allow companies to remotely control their supply chain and effectively manage their entire workflow. With the expected growth of the 3D printing market and the rethinking of supply chains, especially with the pandemic, MakerOS offers an attractive solution for companies in this space.

May: Marklix
3D printing enables on-demand manufacturing at essentially constant and predictable costs, which makes it suitable for small-scale production. For this reason, startup Marklix decided to use additive manufacturing as a production tool for their venture. Their intention is to produce spare parts at a low cost to encourage more people to repair their objects instead of buying new. For this reason, the French company developed their online platform. The online platform allows people to search for the spare parts they need and then manufacture them using 3D printing services. With this development, they became our Startup of the Month in May 2020.

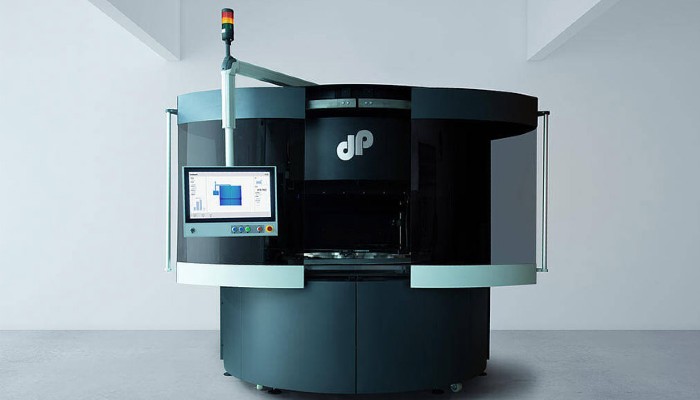
June: dp polar
In June 2020, the German company dp polar was the Startup of the Month. dp polar developed the world’s first AM system with a continuously rotating printing platform for industrial printing called AMpolar® i2. Unlike traditional processes, it is not the print head that moves, but the area being printed on. According to the manufacturer, this should enable high-precision components to be printed up to 20 times faster in larger quantities and with a build volume of approximately 700 liters. In addition, different customer-specific materials are said to be able to be processed in a single pass. In this way, dp polar’s patented system is expected to pave the way from rapid prototyping to industrial series production.

July: CASTOR
Israel-based CASTOR has developed a software solution to help manufacturing companies reduce their 3D printing lead times and production costs. To do this, the 3D printing software performs a technical and economic analysis of CAD files and provides detailed feedback on parts such as the appropriate manufacturing method, printer and material. It incorporates the requirements for the final part, performs optimizations and provides information on costs and delivery times. After that, CASTOR then connects the manufacturer of the part with a suitable 3D printing service. The solution is suitable for beginners as well as experts, as it is easy to use and automates part control processes.

August: Azul 3D
American company Azul 3D was our Startup in August 2020. Since resin 3D printers are limited by their low printing speed and size of the printing roller, the startup developed their HARP technology. Their stereolithography-based large-format 3D printer is said to be able to print adult-sized parts in as little as 2 hours. In doing so, Azul 3D emphasizes that large format does not solely refer to the production of large parts, but also medium size parts in bulk.
September: Metallum3D
Metallum3D specializes in sinter-based additive manufacturing with metal. To improve sintering processes, the company has developed a microwave sintering process. This process uses non-resonant cross-polarized slotted waveguides and granular susceptor materials. This combination is said to make the heating rate 5-10 times faster and the sintering time up to 80 percent shorter than conventional sintering. In addition, the heat is said to be evenly distributed with this process. With its process, Metallum3D aims to open up the possibility of using microwave sintering commercially on a large scale.
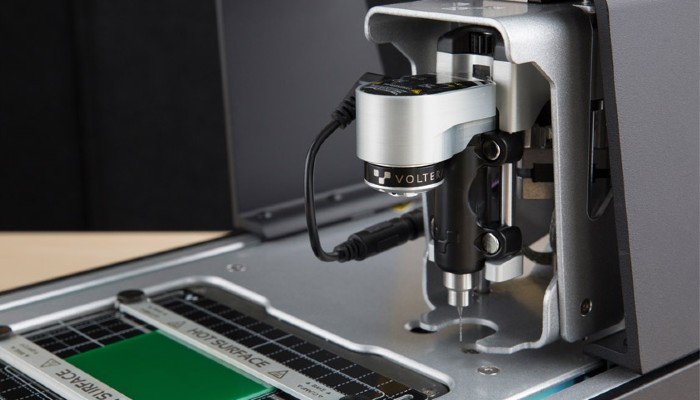
October: Voltera
Microprinting has allowed additive manufacturing to find its place in the electrical industry. Voltera integrated it into their V-One machine to enable 3D printing of circuits. The printing process begins with opening Gerber files, the standard layout format for printed circuit boards, in the CAM software. This converts the input files into toolpaths, the machine calibrates itself and is ready to begin creating the board. Although the V-One is aimed at professionals, its ease of use means it can also be used in universities and schools. In this way, Voltera aims to revolutionize the electronics sector and has thus been our 3D startup of the month in October 2020.

November: Aeditive
Aeditive is a high-tech startup founded in 2019 and based in Norderstedt near Hamburg. Aiming to digitize the construction industry with robotic printing solutions, the company specializes in 3D concrete printing. Their Concrete Aeditor concrete printer can produce concrete parts with maximum dimensions of 11x4x4 meters on a steel pallet using the shotcrete process. In this process, one robot applies the concrete layer by layer, while a second robot finishes surfaces, for example. In this way, Aeditive aims to provide its customers with a high level of automation in concrete part production and, at the same time, more sustainable products through material savings.
December: iFactory3D
Our December 2020 startup, iFactory3D, has developed an FDM printer with an assembly line as the build platform. Called iFactoryOne, this 3D printer is designed to make it possible to mass produce parts of any length, without any interruption. It is suitable for designers, engineers, students, entrepreneurs, healthcare providers and the education sector and is priced at under $1,000. The German company has also equipped the 3D printer with the ability to work without a machine operator and with remote control capabilities. Thus, iFactory3D automates the printing process and enables high-volume production.

Which 3D startup impressed you the most? You can vote HERE for the 3D startup that you think is worthy of the title of Startup of the Year. If you have more to add, let us know in a comment below or on our Facebook and Twitter pages! Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter, with all the latest news in 3D printing delivered straight to your inbox!







very good