Why combine artificial intelligence and 3D printing?

Nowadays, we’ve noticed buzzwords such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Blockchain or Industry 4.0 being increasingly used and thrown around. In themselves, these technologies can have and are having a huge impact on today’s economy and existing production systems. But what about the fact that these new technologies – often described as disruptive – could be combined? Then, will there be completely new, previously unimaginable possibilities?
What interests us above all is of course the combination of these technologies with additive manufacturing. In this piece we explore the link between artificial intelligence and 3D printing. The aim is to understand what possibilities exist when these two technologies are combined, what benefits can be gained? What limitations may remain?

Many new technologies are disrupting current manufacturing techniques
First of all, let’s look at the term artificial intelligence. Dr. Thomas Wilde, mainly active as an entrepreneur and investor, especially in the field of AI software solutions gave us a definition: “AI as a discipline initially includes all the processes that help machines to perceive, think and act like humans. As a result, we are dealing with a very wide range of linguistic processes, image processing, but also processes in the fields of motor skills and robotics“. In our daily lives, it is mainly found in the media and electronics – your smartphone, for example, is able to recognize your face or has a voice assistant that obeys to your voice: Alexa from Amazon, Siri on Apple, Google Now, etc.
Combining artificial intelligence and 3D printing
Artificial intelligence is often linked to terms such as machine learning, neural networks, automation or artificial vision. The idea here is that a machine can solve a given problem by itself, without human intervention, based on data and past experiences. This is of particular interest when combined with 3D printing technologies as it could increase the performance of a 3D printer by reducing the risk of error and facilitating automated production. Indeed, more and more startups and research projects are integrating AI into a 3D printing product or service.

Many electronic devices have integrated AI nowadays
Examples range from automating the entire 3D printing workflow to quality prediction and the development of new materials. We have spoken to some experts who have developed systems in these areas, which are briefly presented below.
Automating the 3D printing workflow
A first application is, for example, the automation of the 3D printing workflow. This comprises various steps, from the creation of the model as a CAD file, to its preparation for printing in a slicing software, to its final printing. AMFG (for Autonomous Manufacturing), a London-based company, offers a solution for this. “With our software solution designed for the 3D printing workflow, we enable the automation of important steps such as production management,” said Keyvan Karimi, CEO of AMFG. Artificial intelligence is used at AMFG to automate manual tasks such as data collection, cost tracking, planning construction. The software can be used to optimize production capacity by improving machine utilization and planning production orders according to availability – all of this is done automatically by artificial intelligence. Material selection can also be automated with AI: depending on the requirements of the part to be printed, the software makes recommendations on the material to be used to achieve the best result.
However, Kevan Karimi adds: “We are still a long way from using artificial intelligence to control the entire additive manufacturing process“. We are now able to automate certain steps, but we will still need human intervention for some individual tasks, such as post-processing, which is still time-consuming – which is why it is important to minimize it by working efficiently on the 3D file.
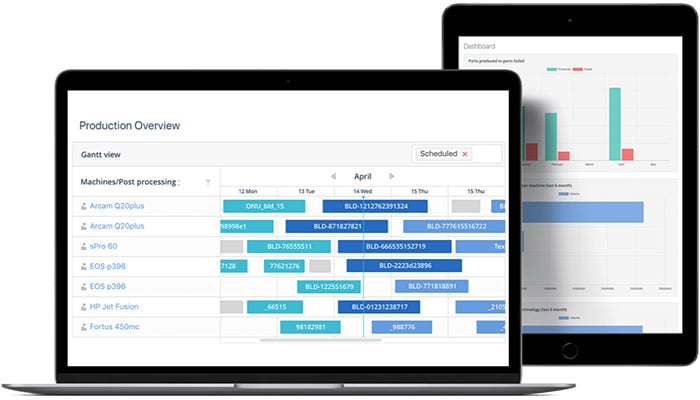
AMFG’s solution can be used to automate production workflows
Expanding the range of materials
The combination of artificial intelligence and 3D printing can also help to broaden the range of compatible materials and thus meet the requirements of industrial sectors such as aerospace, which most often require high-temperature materials. The futureAM project launched by the Fraunhofer Institute IWS in 2017 is a perfect example of this. Prof. Ing. Frank Brückner, Head of the Business Area Generating and Printing at Fraunhofer IWS and AMCD (Additive Manufacturing Center Dresden), explains: “Aircraft engines could operate at higher temperatures and more efficiently if most materials did not fail at temperatures above 1200 degrees.”
Where does AI come in? The professor told us: “The processing of new high-performance materials is very complex and requires fine tuning of all process parameters. That’s why we monitor the 3D printing process with a variety of different sensors. Using AI, we then evaluate this data stream and identify hidden relationships that are not recognizable to humans.” This is precisely where the advantage of artificial intelligence lies: it is able to process very large volumes of data quickly, a task that is far too tedious for humans. Thanks to this work, researchers can process complex alloys and maintain material properties.
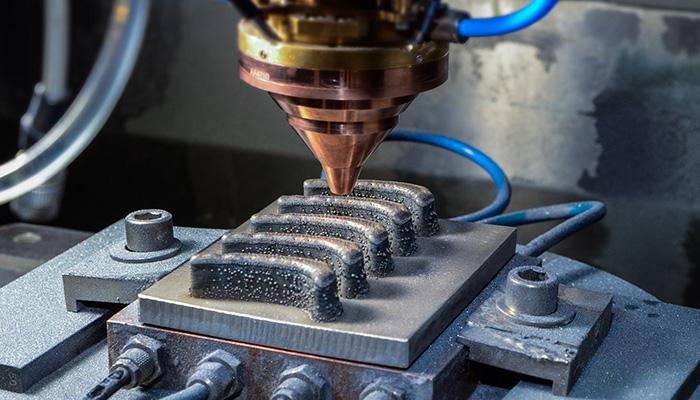

3D printed turbine blades printed | Credits: Fraunhofer IWS
Optimizing the 3D printing process
AI can also help improve the 3D printing process. For example, the printability of an object can be analyzed before starting any process. The quality of a part can also be predicted and the process can be controlled to avoid printing errors, effectively saving time.
This is exactly what the startup Printsyst is trying to do with its AI engine, especially in the aerospace industry. The objective of the company’s patented AI algorithm is to identify the functionality of parts and improve the print success rate. This solution builds on the experience gained from previous projects that have successfully integrated additive manufacturing. For example, it uses print parameters that have worked well, with which it can accurately estimate component costs, manufacturing and delivery times, etc., and it can be used to improve the quality of the printed product. Above all, this increases productivity and reduces the risk of errors, which can be very costly, especially in the aerospace sector.
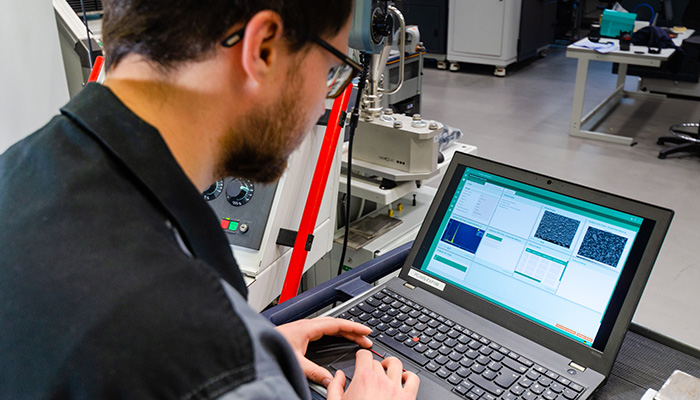

Data is collected in the IWS database and processed for AI | Credits: Frauhofer IWS
Eitan Yona, co-founder of Printsyst, explains: “We reduce the average 3D print preparation process from 30 minutes to 5 seconds for each individual job. By reducing this time, we increase printer utilization and by eliminating errors, we reduce iterations.” The use of AI reduces the complexity of a traditionally manual process and provides better results.
Optimization also involves a printability analysis, also known as pre-print part evaluation. Typically, AMFG has included a feature in its software package that ensures that a part to be manufactured is truly suitable for 3D printing, whether in terms of stability, shape or resilience. This is particularly important for companies that want to work effectively with additive manufacturing. Keyvan Karimi sums up: “We want to use AI to improve our software so that 3D printing departments can effectively control their production processes and guarantee the accuracy and quality of the parts they produce. This is becoming increasingly important as the industry continues to move towards the production of finished parts.”
While there are many examples and various benefits, let us nevertheless ask ourselves the question of the risks associated with the combination of artificial intelligence and 3D printing: should we fear the dangers associated with them?
Are AI and additive manufacturing a threat?
Any new technology brings with it its own set of limitations and can present a number of risks. AI and additive manufacturing are no exception: in the 3D printing market alone, we are talking about 3D printed guns for example. And when it comes to artificial intelligence, we often hear that machines could overtake humans. However, 3D technologies today make it possible to easily reproduce many objects. If we incorporate artificial intelligence into these, our privacy and safety could be seriously compromised in the future. Take the example of the Astro dog, which was designed using 3D printing and has an AI-based brain: its decisions are based on environmental influences. What will happen if these choices go beyond the human imagination? Could we lose control of such a robot? Should we then fear the dangers of both technologies?
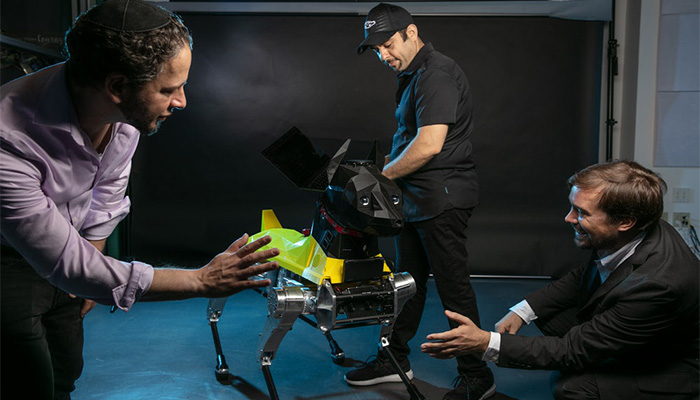

The Astro dog has been 3D printed and can move thanks to AI
Eiton Yona of Printsyst adds that artificial intelligence simplifies the use of additive manufacturing so that technological understanding is no longer necessary. He says, “You can print a weapon on one side and human bones on the other.”
Let’s not see the glass half empty: Artificial intelligence and 3D printing have a bright future ahead of them! Keyvan Karimi from AMFG confirms: “We believe that AI, machine learning and other technologies in Industry 4.0 have real potential to improve the manufacturing process and allow engineers and operators to spend less time on repetitive manual tasks and more time on value-added processes. In fact, we are just scratching the surface of what is possible with these technologies.”
Artificial intelligence and 3D printing: the combination of the future?
We are certain that both technologies will play a major role in the coming years, especially in industrial applications. For Eiton Yona of Printsyst, artificial intelligence and 3D printing are more connected than one might think: “Today’s additive manufacturing requires a high degree of specialized knowledge for the production of parts. AI will adopt important rules in the 3D printing workflow. Faster and smarter algorithms will reduce the manual process performed by humans. AI will then allow access to large amounts of data to better manage 3D technologies.”
The solution developed by AI Build makes it possible to correct printing errors in real time | Credits: AI Build
At the moment, this combination is in its infancy and already shows great potential: the few examples cited show you how AI and 3D printing stimulate innovation, make production more efficient and give companies a competitive edge. We don’t yet know how far this revolution will go, but one thing is certain: it is promising.
What do you think of artificial intelligence and 3D printing coming together? Let us know in a comment below or on our Facebook and Twitter pages! Sign up for our free weekly Newsletter, all the latest news in 3D printing straight to your inbox!







