#3Dstartup: Metallum3D offers microwave sintering for metal AM
In recent years, the metal additive manufacturing segment has experienced a strong growth, explained in great part by the arrival of players who wanted to make it more accessible to users. These players have offered technologies close to MIM or Binder Jetting, i.e. indirect metal 3D printing processes. The latter is based on the use of metallic powders and a binder, which is then eliminated during the debinding stage. The part must then be sintered in a suitable furnace to weld the metal particles together, giving the part its desired properties. These two post-processing steps are crucial and quite technical. For example, sintering requires temperature control: the part must heat up sufficiently to ensure that the powder particles are fully welded without causing deformation. Metallum3D has addressed these constraints and developed a microwave sintering system, a process that offers a number of benefits for these metal AM processes. We met with its founder and CEO, Nelson Zambrana, to find out more!
3DN: Can you present yourself and your relationship with AM?
I am an engineer with a passion for business. Over the past 25 years I’ve worked in the electronics, pharmaceutical and medical device industries having implemented multiple manufacturing processes including additive manufacturing, CNC machining, injection molding, laser machining and others. Since founding Metallum3D in 2016, I’ve concentrated my efforts in the development of microwave sintering technologies for sinter based metal additive manufacturing.
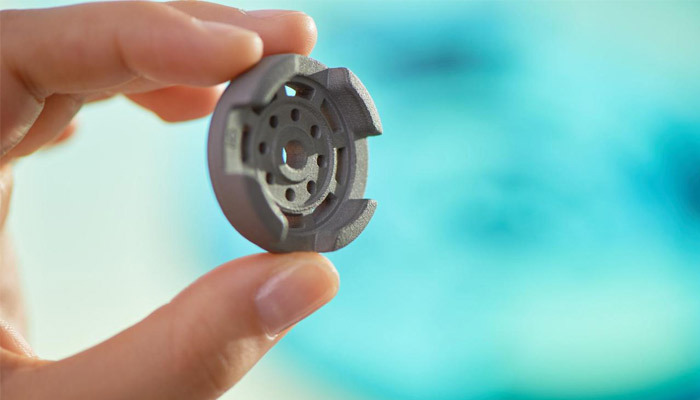

Metallum3D develops microwave sintering technologies for sinter based metal additive manufacturing
3DN: Why and how was Metallum3D founded?
Metallum3D was founded with a focus in the development of microwave sintering technologies for sinter based metal additive manufacturing. Sintering processes play a major role in metal additive manufacturing and over the last 40 years the performance of conventional sintering processes has not significantly improved. Current conventional sintering processes for sinter based metal additive manufacturing have slow heating rates (~ 5 deg. C/min), long sintering times (> 24 hrs.), high energy consumption and high equipment costs. Microwave sintering has the potential to greatly improve the performance and economics of the sintering process including fast heating rates (5x to 10x faster), short sintering times (up to 80% reduction when compared to conventional sintering), lower energy consumption and lower equipment costs.
Despite many potential advantages, there are two primary problems associated with microwave sintering. The first problem is that microwave sintering systems operating in a multi-mode resonant condition suffer from uneven microwave energy distributions, which leads to non-uniform heat distributions. The second problem is that parts undergoing microwave sintering exhibit volumetric heating resulting in a reverse heating profile where the inside of the part is hotter than the outside of the part. Since heat uniformity is one of the most critical sintering parameters, these two problems have prevented microwave sintering from being used on a large scale commercial basis. Metallum3D is developing new patent pending microwave sintering technologies that provide the heat uniformity necessary for use in sinter based metal additive manufacturing applications.
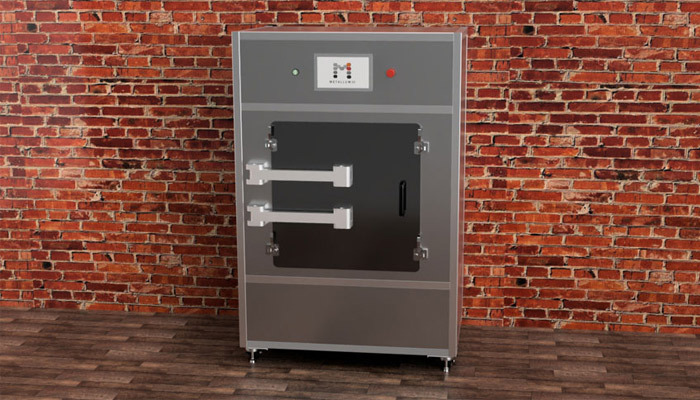

The Metallum3D system
3DN: Can you tell us how your system works? Is it compatible with all materials?
Current microwave heating processes are primarily based on multi-mode resonant technology. This technology has found enormous success in low power, domestic microwave oven applications due to its robustness and simplicity. One major drawback of this technology is the uneven distribution of the microwave energy which leads to non-uniform heating during processing. Several methods including mode stirrers and turntables have been developed to improve microwave energy distribution, but these methods are marginally effective when applied to microwave sintering processes. Metallum3D is developing a new and innovative microwave sintering process that utilizes non-resonant, cross polarized slotted waveguides and granular susceptor materials. This combination overcomes the limitations of multi-mode resonant technology and provides for homogenous heat distributions during microwave sintering.
Metallum3D’s microwave sintering furnace is being designed to be compatible with sinter based additive manufacturing equipment from HP, ExOne, Markforged, Desktopmetal and Xjet.

3DN: Any last words for our readers?
Metallum3D is working to to greatly improve on the performance and economics of sinter based metal additive manufacturing by providing the following:
– Fast heating rates (5x to 10x faster than conventional sintering)
– Uniform heat distribution
– Short sintering times (Up to 80% reduction when compared to conventional sintering)
– Optimal microstructure (smaller grains due to shorter sintering time)
– Energy efficiency
– Lower equipment costs
You can find more information on Metallum3D’s website HERE.
What do you think of Metallum3D’s technology? Let us know in a comment below or on our Facebook and Twitter pages! Sign up for our free weekly Newsletter, all the latest news in 3D printing straight to your inbox!







Could I get some technical information about your microwave system?