Everything You Need to Know About 3D Printing with Nickel Alloys

Nickel alloys have become increasingly important in 3D printing due to their thermal and mechanical strength as well as their resistance to corrosion. These qualities make them an ideal choice for producing high-performance components in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and oil and gas. Their ability to withstand extreme conditions, along with their compatibility with additive manufacturing, allows for the creation of complex, highly specialized parts. In this guide, we’ll explore the properties of nickel alloys, their advantages in 3D printing, key applications, and leading manufacturers in the industry.
Material Properties
The nickel alloys used in manufacturing are derived from nickel ore. This material occurs naturally in ores such as pentlandite, limonite, and garnierite, and is extracted through large-scale mining operations. Once mined, the ore undergoes several refining stages to produce high-purity nickel, which serves as the base for creating specific alloys.

A nickel alloy in powder form. (Credit: Guangzhou Sailong AM Co.)
Some of the most well-known alloys in the industry are named after the companies that patented them. Among the most common are:
- Inconel® – This is a family of nickel-chromium-based superalloys known for their excellent resistance to corrosion and high temperatures. The leading grades are Inconel 625 and Inconel 718, with the main differences lying in their composition. Inconel 625 contains around 58% nickel along with high levels of chromium, molybdenum, and niobium. Inconel 718 has a similar nickel base but includes more iron, less molybdenum, and significant amounts of niobium, aluminum, and titanium.
- Hastelloy® – An alloy composed of cobalt, chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, offering exceptional corrosion resistance in acidic and chemical environments. Hastelloy X is an austenitic alloy with small amounts of cobalt, molybdenum, and tungsten. It provides excellent oxidation resistance at high temperatures, making it ideal for use in jet engines and industrial furnaces.
- HAYNES® – A family of nickel-based superalloys developed by Haynes International, a company specializing in high-performance materials for extreme conditions. Popular grades include 230, 282, and 214, all known for their high heat resistance and structural stability.
In addition to these three, there are other notable alloys such as Monel (nickel-copper), Kovar (nickel-iron-cobalt), and Invar (nickel-iron, typically 36% nickel). All are highly resistant to corrosion in demanding environments, making them ideal for applications in marine, aerospace, and the production of electronic and magnetic components.

3D printed part made from Inconel 625. (Credit: ExOne)
3D Printing with Nickel Alloys
To be used in 3D printing, nickel must first be converted into a high-quality metal powder. This is typically done through atomization techniques, with gas and plasma atomization being the most common methods. Once the powder is produced, it undergoes sorting and conditioning processes. Thanks to these advanced techniques, nickel alloys in powder form are able to meet the strict standards required by the most demanding industries.
3D printing with nickel alloys is primarily carried out using powder-based metal additive manufacturing technologies. The most widely used methods include Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF), Electron Beam Melting (EBM), and Directed Energy Deposition (DED). Each of these processes requires careful optimization of parameters such as laser or electron beam power, scan speed, and layer thickness to ensure the desired quality and material properties in the finished parts. In Metal Binder Jetting, the choice of a suitable binder is critical for layer adhesion. Since the printed parts are highly porous before sintering, it’s also essential to control binder distribution and powder density in order to minimize shrinkage and deformation during the sintering phase.
Advantages and Limitations
These alloys, when combined with additive manufacturing, offer numerous advantages. Thanks to their high temperature resistance, they maintain structural integrity even in environments exceeding 700°C. This makes them an excellent choice for components exposed to extreme conditions. At the same time, 3D printing allows for significant design flexibility, enabling the creation of complex, optimized geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. As a result, more efficient and lightweight parts can be produced, which is an essential factor for many applications in industries such as aerospace and automotive.
However, nickel alloys also come with certain limitations. One of the main drawbacks is their high cost. The price of nickel alloy powder can significantly increase production expenses and may present a barrier to entry. In addition, printed parts typically require post-processing, such as heat treatment and machining, which can extend production times. Handling fine metal powders also poses health and safety risks, requiring strict control measures and the use of appropriate protective equipment.
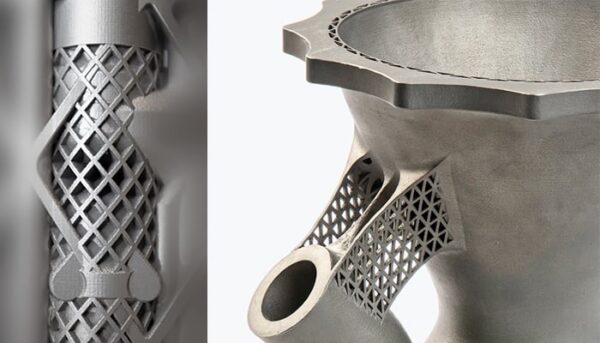
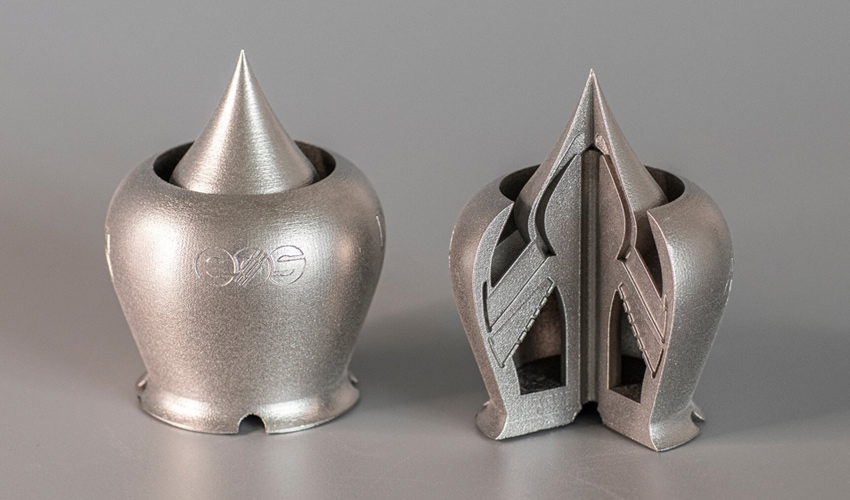
Credit: EOS (left) / Materialise (right)
Key Applications
Nickel alloys in 3D printing are used across various industries thanks to their remarkable properties. In aerospace, they’re employed to manufacture engine components like turbine blades and combustion chambers, parts that need to withstand high temperatures and mechanical stress. In the automotive sector, they’re used for high-performance parts such as turbochargers and exhaust systems, benefiting from their heat and corrosion resistance. In the medical field, their durability makes them ideal for producing implants and custom medical devices. In the oil and gas industry, they’re utilized to make components for drilling and processing equipment, designed to operate in highly corrosive environments and at elevated temperatures. Beyond these, many other industries are already taking advantage of nickel alloys in 3D printing.
Have you had any experience with 3D printing using nickel alloys? Let us know in a comment below or on our LinkedIn or Facebook pages! Plus, don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter to get the latest 3D printing news straight to your inbox. You can also find all our videos on our YouTube channel.
*Cover Photo: EOS








I love your post.
Hello,
Can you print Nickel 200 or 201?